Cube View Conditional Formatting
Cube View Conditional Formatting provides the ability to format Headers or Cells based on defined criteria. The application of Conditional Formatting will be applied and is visible in Data Explorer, Excel and Reports views. The Conditional Formatting criteria is applied to Cube View Rows or Columns on the Formatting Property within the Cube View Editor.
The Conditional Formatting is available on the formatting elements of a Cube View.
-
Cube View Default Formatting
-
Row / Column Headers
-
Row / Column Data Cells
-
Row / Column Overrides
The Conditional Formatting follows the Cube View Processing order of operations as:
-
Number Format as defined in Application Properties
-
Cube View Default
-
Column Formatting
-
Row Formatting
-
Column Overrides
-
Row Overrides
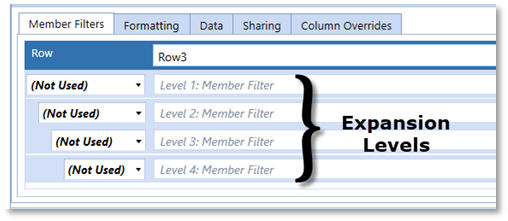
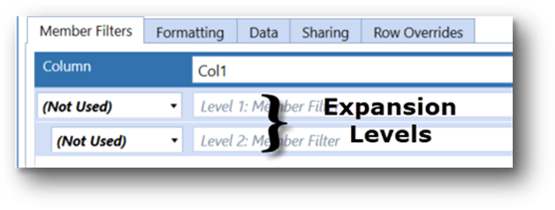
The combination of formats and overrides equals the format for the cell when rendered. Formatting can be applied, and isolated to, the nested Expansion Levels on rows and/or columns by using Property Filters found in the Conditional Formatting dialog box.
This feature is a Cube View formatting option. It is not available as a Standard Reports setting found in Application Properties.
Formatting can be applied, and isolated to, the nested, Expansions, on rows and/or columns by using Filters found in the Conditional Formatting dialog box.
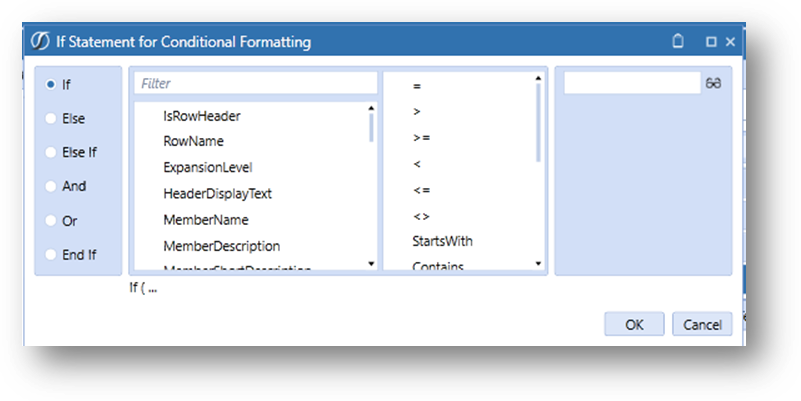
Conditional Formatting Dialog Box
Formatting, Conditional or general, can be applied directly to the Formatting dialog text box. The Conditional and Format buttons launch additional dialog boxes as a graphical interface to available formatting options. The Conditional Formatting Dialog Box is divided into four sections to assist the developer in defining formatting criteria.
-
If/Then – Defines options for Conditional Statements to apply constraints to formatting
-
Properties – Allowable filtered property elements for formatting
-
Operators – Available test Property Filters
-
Text/Object – Text object to be tested. If the Text/Object result is a reserved word such as “If”, “Else”, “ElseIf”, “Then”, “End If” or other Operators as “In”, the text must be enclosed in square brackets: [ ].
|
Header Property Filters |
Description |
|---|---|
|
IsRowHeader |
Boolean, determines if object is a Row Header field (appropriate if applying to Cube View Default) |
|
IsColHeader |
Boolean, determines if object is a Column Header field (appropriate if applying to Cube View Default) |
|
RowName |
Reference a Cube View Row Name |
|
ColName |
Reference a Cube View Column Name |
|
ExpansionLevel |
Cols/Rows, determine the expansion level for rows (1-4), columns (1-2) related to isolating the row expansion headers |
|
HeaderDisplayText |
Reference custom descriptions used with the :Name() function |
|
MemberName |
Reference metadata member label |
|
MemberDescription |
Reference metadata member description |
|
MemberShortDescription |
Reference metadata member short description (Applies only to Time dimension) |
|
IndentLevel |
Reference the indentation level. This is derived from manual formatting settings or via the system generated indents from tree expansions. Zero-based, meaning if there is no indenting, the value is zero. The next level of indentation is 1, etc. |
|
Expansion Specific Property Filters |
Options |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
RowE expansion level - criteria |
Row Expansions 1 through 4 |
Provides the ability to identify nested/expansion rows with specified criteria |
|
ColE expansion level - criteria |
Column Expansions 1 and 2 |
Provides the ability to identify nested/expansion rows with specified criteria |
| Cell Format Property Filters |
Description |
|---|---|
|
IsNoData |
Test for no data |
|
IsRealData |
Test for stored data, ignores derived Zero-View data |
|
IsDerivedData |
Test for derived data, commonly resulting from Scenario Zero-View settings |
|
IsRowNumberEven |
Test for the Row number, as expansions or fixed rows |
|
ExpandedRowNum |
Test count of expanded rows. Zero-based. This Property Filter is based on the total Cube View count of rows generated from each row and its expansions. |
|
CellAmount |
Test cell data amount |
|
CellStorageType |
Tests the method used to store data. Available DataCellStorageType objects are NotStored, StoredButNoActivity, Input, Journals, Calculation, Translation, Consolidation, DataCellDetailYTD, DataCellDetailPeriodic, DurableCalculation. |
Examples Applying Conditional Formatting
Below are common usage examples of Conditional Formatting.
Indent Level
The IndentLevel Property Filter will dynamically format from defined rows or expansions. Indentation is zero-based. The formatting can be applied to the default or to Rows. This solution can speed formatting for summary level dimension members.
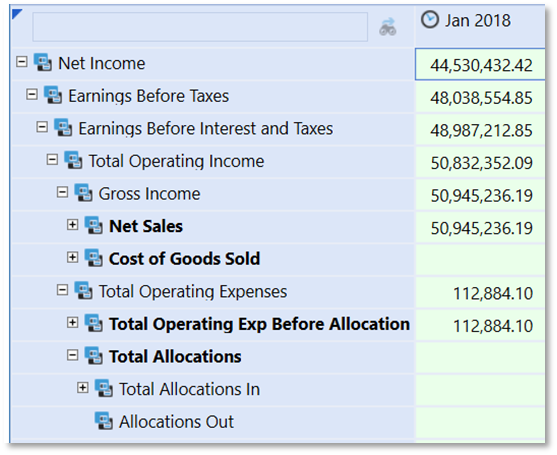
Apply the formatting to the Header section of the Cube View Default or to specific Rows.
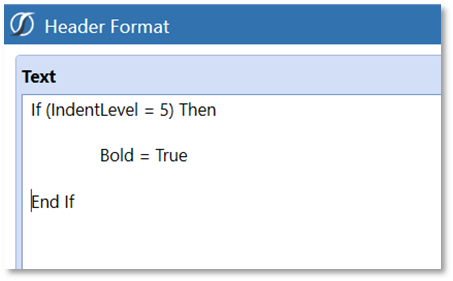
Examples of Using Conditional Property Filters Conditional “Traffic-Lighting”
“Traffic-Lighting” is data related and therefore applied as a Cell Format. The designer has a choice to apply the conditional formatting to either a Row or a Column. The order of operations for formatting can impact the decision. Row overrides are the final layer of formatting applied to a Cube View and would not be impacted by other more general formatting.
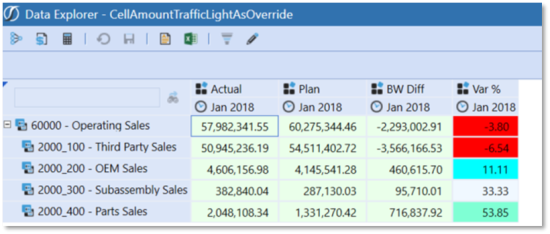
1. Conditional Formatting can be applied to the rows or columns. A definition applied to the row Formatting tab would apply to all columns. A row Override would isolate the formatting to a specified column(s).
2. The CellAmount Filter is used within multiple If/ElseIf statements to define the various tests required for the report.
ExpandedRowNum Expansion Range
Conditional Formatting provides the ability to Format an expanded range of data cells using the ExpandedRowNum Property Filter. This is useful in formatting to support “Top 10” type reports. This Property Filter best supports Cube View designs that use known expansions, such as Ranking Business Rules or Member Lists. If applied to specific rows, the formatting applies to the defined row, but the Expansion Number Reference relates to the entire Cube View. Formatting defined on subsequent rows will be impacted if the expansion members change on previous rows. The ExpandedRowNum Property
Filter can also be applied as a Default Cube View format, in which the definition will apply to all rows. This would require If/ElseIf type statements to support all rows.
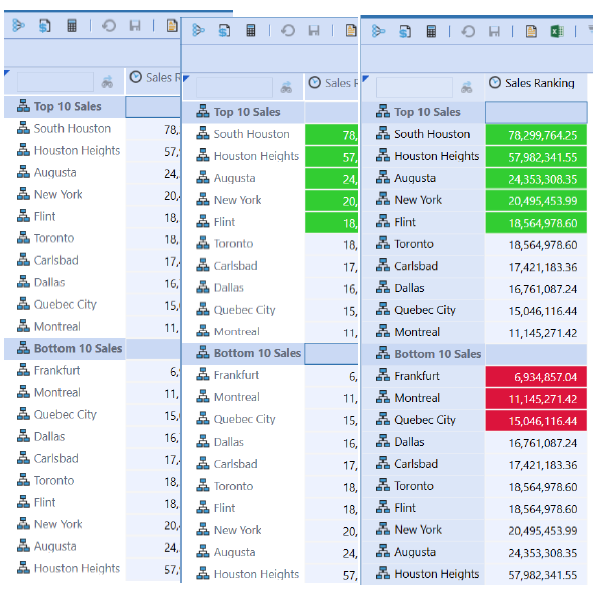
1. Design or open a report which supports formatting for ExpandedRowNum , such as a ranking report in the example.
2. Determine how the formatting should be applied, as a default, row or column. The example will use the Cube View Default Formatting.
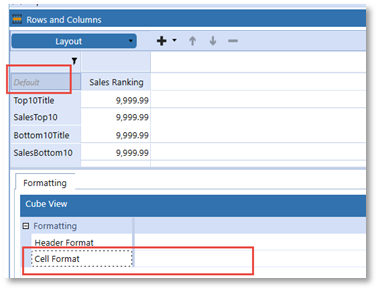
3. Cell Format is applied for Conditional Formatting using the ExpandedRowNum filter. Being zero-based, and having to account for each row and its expansions:
-
Condition1 – Rows < 6 is defined because the text header row “Top10Title” initiates the count at zero.
-
Condition2 – Rows > 11 and < 15 is defined because all the rows up to Row4, “SalesBottom10”, reflect rows 0-11 on the Cube View. The conditional row references must reflect all the Cube View Expansions.
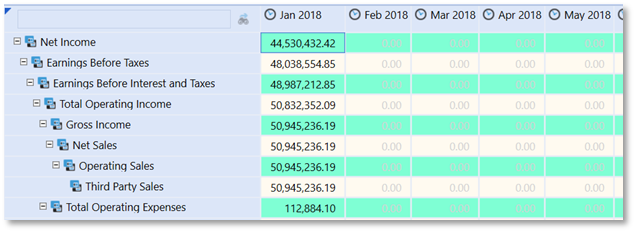
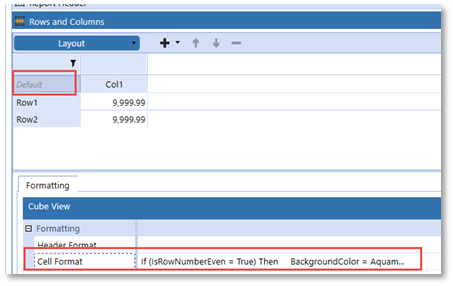
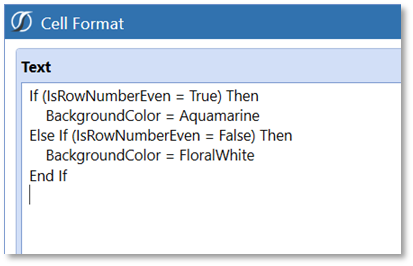
Test for Row IsRowNumberEven
The IsRowNumberEven Property Filter may be useful to vary formatting by the even/odd numeric expansion of rows on a cube view. For example, to replicate a “green-bar” style report the IsRowNumberEven would be a suitable Property Filter.
-
In this example the formatting can be applied to the Cube View Default Cell Format since it will globally apply to all rows.
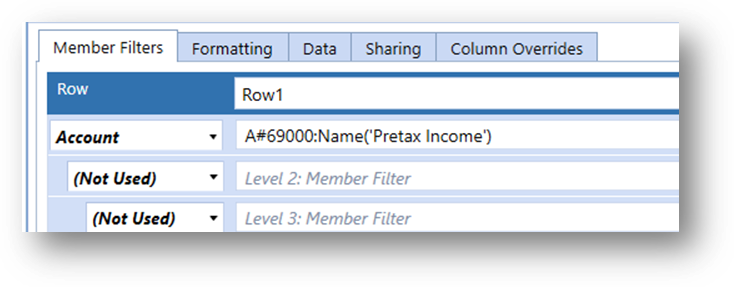
MemberName, MemberDescription or HeaderDisplayText
The ability to format based on the Name or Description is greatly enhanced by adhering to a standardized metadata naming convention. Summary level members having keywords such as “Total” or prefixes or suffixes such as “Tot” could be used in Conditional Formatting. Members could be formatted using dynamic criteria, such as StartsWith or EndsWith.
HeaderDisplayText differs from the MemberName and MemberDescription Property Filter in that it references the custom Name parameter in a Member Filter.
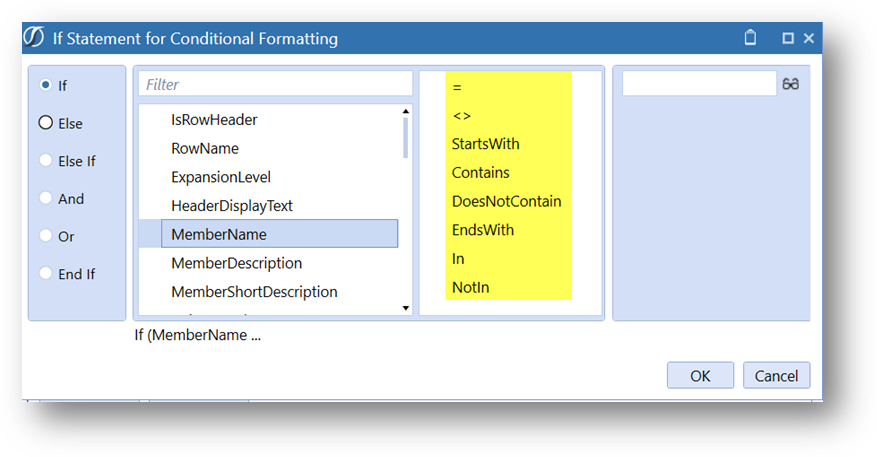
Dynamic Criteria can be applied to the Name and Description Property Filters to apply the required formatting.
-
Apply Conditional formatting to Row Header.
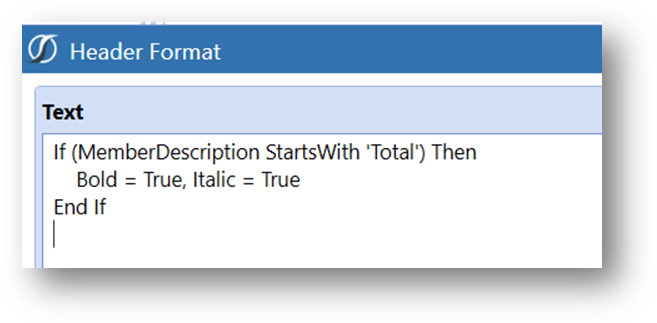
The result is a dynamically formatted report.
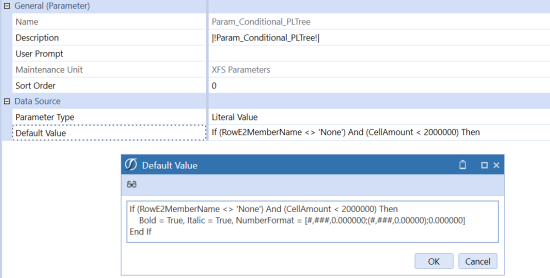
Parameter Formatting
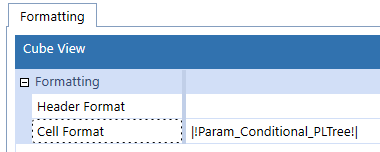
Conditional Formatting definitions can be applied to a Cube View as a Literal Parameter. To apply, select the Format string from the Cube View, Copy (Ctrl-C), select the Default Value property of a Literal Value-type Parameter and Paste (Ctrl-V). Once saved, this Parameter can be referred to in a Cube View Format. Per the example below, the reference of |!Param_Conditional_PLTree!| in a Cube View Format would apply the associated Format string.